Research Introduction
Gene regulation by peptide nucleic acid (PNA)
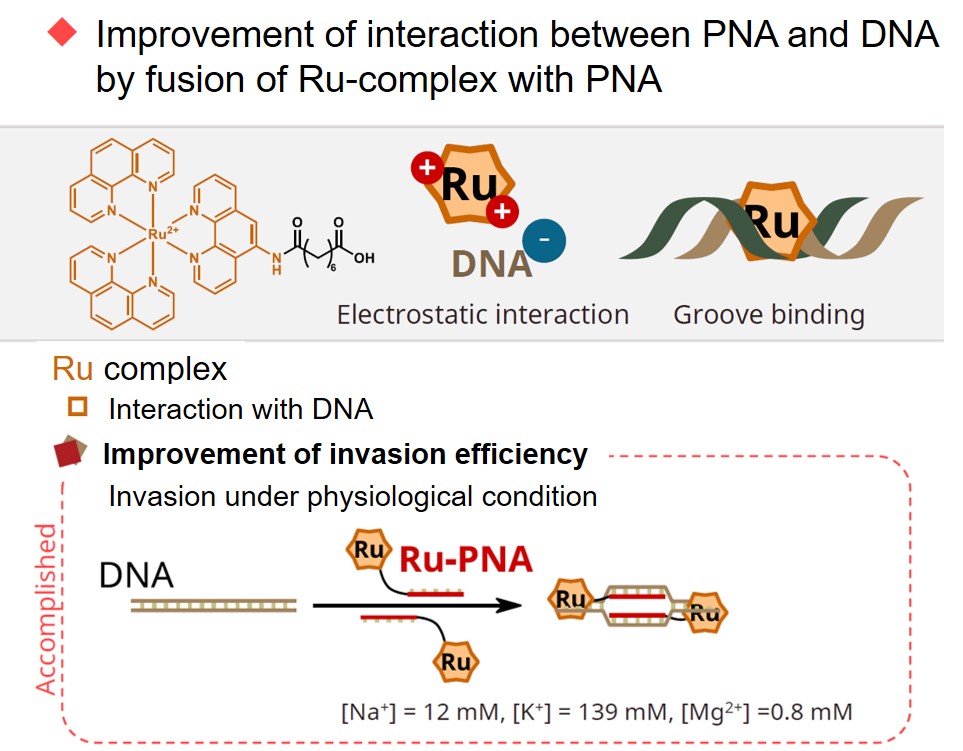
Episode 1: Improvement of PNA invasion efficiency by conjugation with ruthenium complexes
PNA has an attractive feature called double duplex invasion, which selectively binds to double-stranded DNA, but there are several issues with its application in vivo. One of these is low invasion efficiency in the in vivo environment. In the in vivo environment, the salt concentration is very high, suppressing charge repulsion. Typically, DNA/DNA duplexes are unstable due to electrostatic repulsion caused by the negative charge of the phosphate backbone of DNA. However, in a high salt environment, the electrostatic repulsion is alleviated, making the DNA/DNA duplex stronger. This results in a problem of low efficiency of PNA invasion based on DNA/PNA interaction.
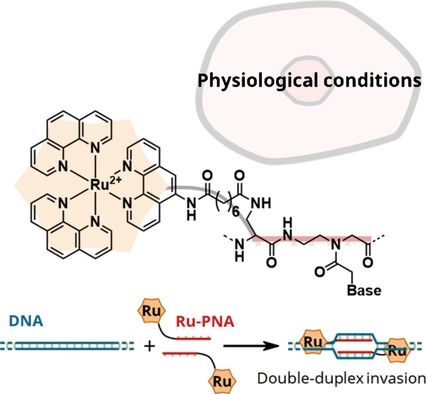
To solve this problem, we focused on the ruthenium complex (Ru(phen)3), known to have hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions with DNA. We designed a ruthenium complex-containing PNA to enhance the DNA/PNA interaction. Interestingly, the invasion efficiency changed depending on the position of the ruthenium complex introduced into the PNA and the length of the linker. The ruthenium complex-linked PNA having optimal molecular design can invade the target DNA double helix's target sequence and form a stable invasion complex as expected, even in a high salt concentration in vivo environment. Generally, increasing the binding strength with the target DNA often increases the probability of undesired binding to sequences other than the target sequence. However, the ruthenium complex-linked PNA in this research recognized a single base mismatch and did not form any invasion complexes.
Please refer to this paper for details.
- M. Hibino, Y. Aiba, Y. Watanabe, O. Shoji "Peptide Nucleic Acid Conjugated with Ru‐complex Stabilizing Double‐Duplex Invasion Complex Even under Physiological Conditions" , ChemBioChem, 19, 1601-1604(2018).
https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201800256
Episode 2: Cationic guanine-introduced PNA (masaPNA) by methylation of guanine


