Research Introduction
Gene regulation by peptide nucleic acid (PNA)
Episode 4: Highly efficient invasion of mismatched PNA into mismatched sites of double-stranded DNA
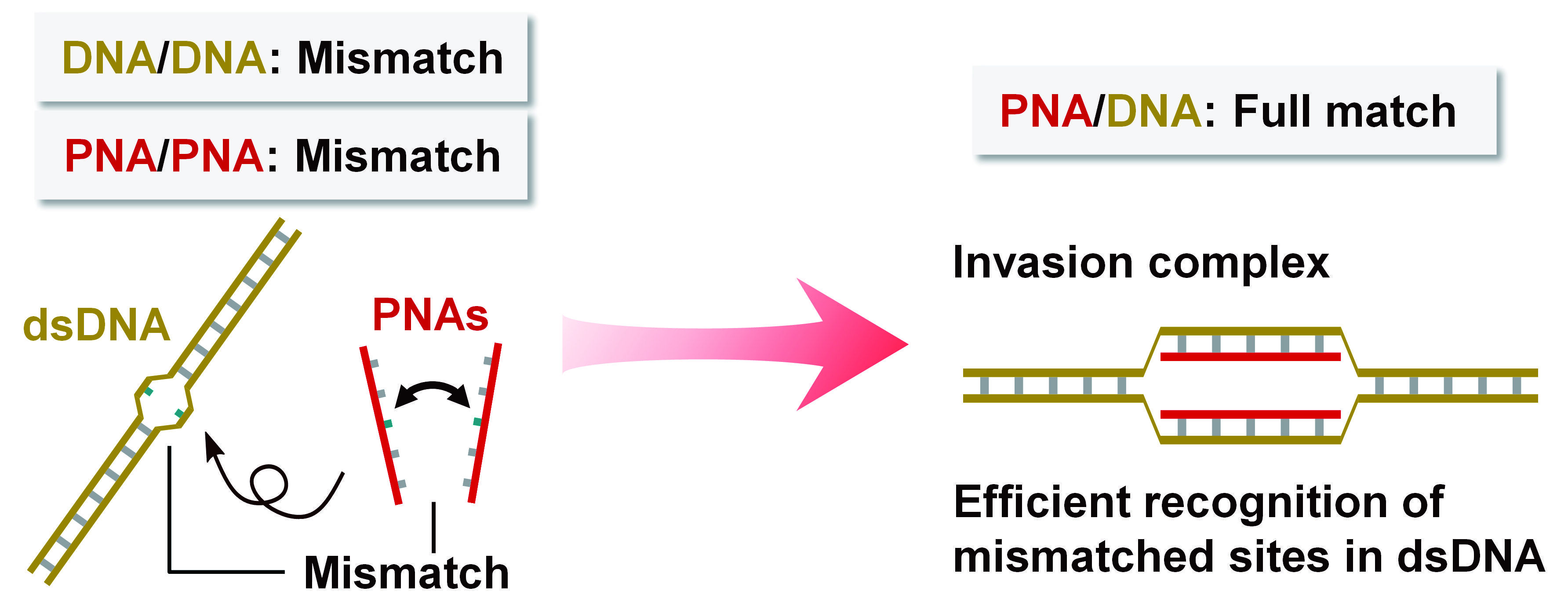
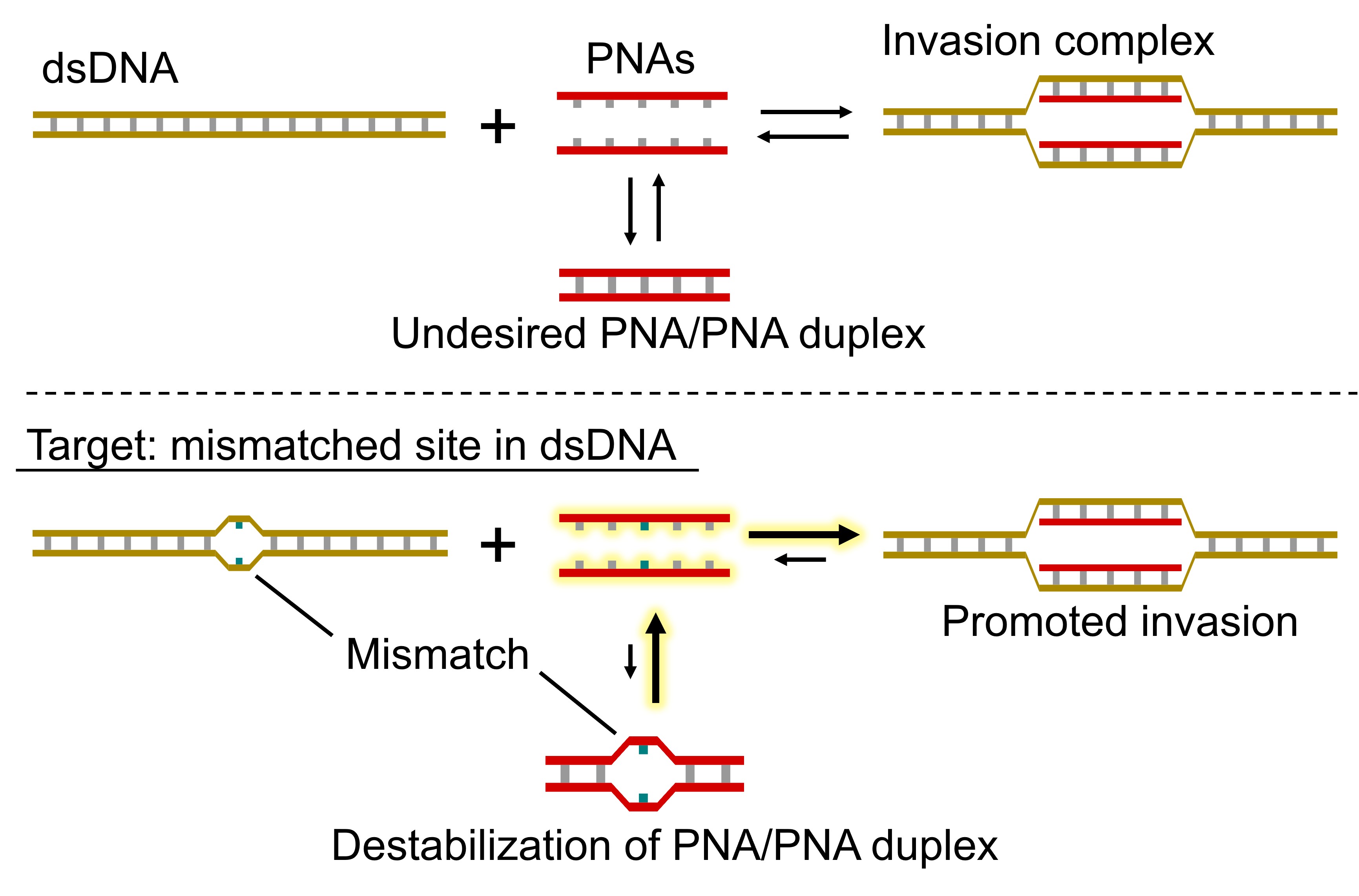
The most remarkable feature of PNA is its ability to invade double-stranded DNA in a sequence-selective manner. However, since it targets complementary double-stranded DNA, the two PNAs must have complementary base sequences. Therefore, forming a more stable PNA/PNA duplex is more effective than forming an invasion complex by DNA/PNA interaction. We have previously demonstrated that the destabilization of the PNA/PNA interaction by introducing cationic guanine improves the invasion efficiency(Episode 2: Cationic guanine-introduced PNA (masaPNA) by methylation of guanine).
Based on this knowledge, we achieved highly efficient invasion by destabilizing PNA/PNA by introducing mismatches into two PNAs and further targeting mismatch-containing double-stranded DNA. Previous PNA-based invasion of double-stranded DNA required excessive PNA relative to DNA. However, this system achieved nearly quantitative invasion even with a 1:1 ratio of PNA to DNA. Although the target is limited to mismatch-containing double-stranded DNA, such DNA mismatches are often associated with severe genetic diseases. This system is expected to be applied to detect DNA mismatches.
Please refer to this paper for details.
- M. Shibata, O. Shoji, Y. Aiba, "Recognition of mismatched sites in double-stranded DNA by a pair of partially noncomplementary peptide nucleic acids" , Chem. Lett., 53, (2024) upae234
https://doi.org/10.1093/chemle/upae234