Research Introduction
Artificial metalloproteins based on heme acquisition protein HasA
Episode 4: Photosterilization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by HasA capturing gallium phthalocyanine as photosensitizer
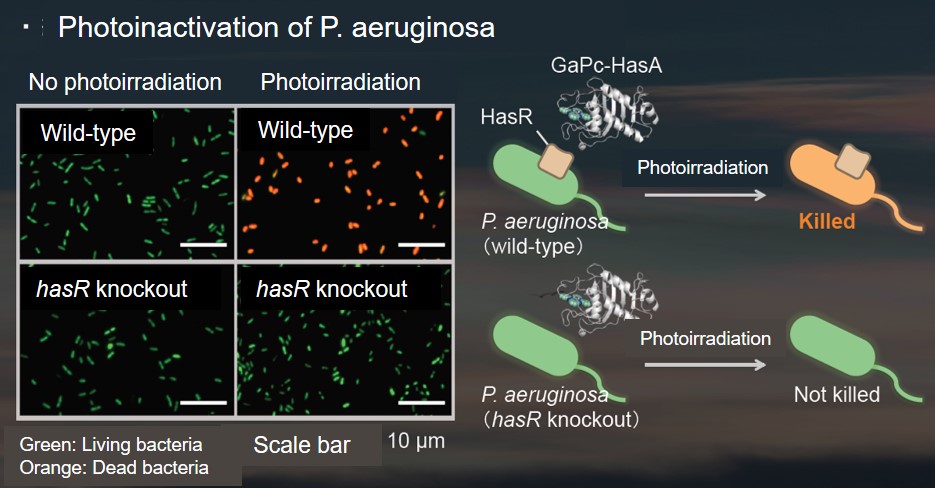
FePc-HasA blocked the P. aeruginosa receptor HasR, thereby inhibiting its ability to acquire iron and suppressing its growth, but P. aeruginosa was not killed (bacteriostatic effect). Therefore, to achieve a more effective treatment, we aimed to develop a system that would hijack the iron acquisition system of P. aeruginosa and sterilize the P. aeruginosa cells.
Therefore, we focused on a gallium complex of phthalocyanine (GaPc), which can absorb red light and generate singlet oxygen, which is highly cytotoxic. When GaPc is complexed with HasA and added to P. aeruginosa, GaPc is transferred from HasA to HasR on the P. aeruginosa, just as with FePc-HasA. When P. aeruginosa is irradiated with red light in this state, singlet oxygen is generated within the P. aeruginosa, and the toxicity of this oxygen kills the P. aeruginosa. The efficiency was also high; more than 99.99% of P. aeruginosa bacteria could be killed with 10 minutes of light irradiation. Furthermore, a light sterilization method using GaPc-HasA also successfully killed drug-resistant P. aeruginosa.
In addition, since humans do not have HasR, we are expected to be less damaged by this photosterilization treatment. Furthermore, bacteria other than Pseudomonas aeruginosa have the HasA-HasR pair, but each bacterium has its unique HasA-HasR pair to avoid confusion. Thus, by using HasA from Pseudomonas aeruginosa, we are expected to specifically kill only Pseudomonas aeruginosa without affecting other resident bacteria (such as good bacteria necessary for maintaining health). We are currently researching to put this into practical use as a potent treatment that can treat drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa without side effects.
Please refer to this paper for details.
- Y. Shisaka, Y. Iwai, S. Yamada, H. Uehara, T. Tosha, H. Sugimoto, Y. Shiro, J. K. Stanfield, K. Ogawa, Y. Watanabe, O. Shoji, "Hijacking the Heme Acquisition System of Pseudomonas aeruginosa for the Delivery of Phthalocyanine as an Antimicrobial", ACS Chem. Biol., 14, 1637–1642 (2019).
https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.9b00373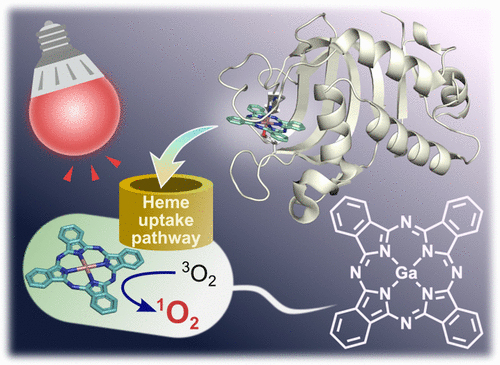
Episode 5: Complexation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa HasA with 5-oxaporphyrinium cation complex


