Research Introduction
Gene regulation by peptide nucleic acid (PNA)
Episode 3: Improved invasion efficiency of PNA by linking nuclear localization signal peptide (NLS)
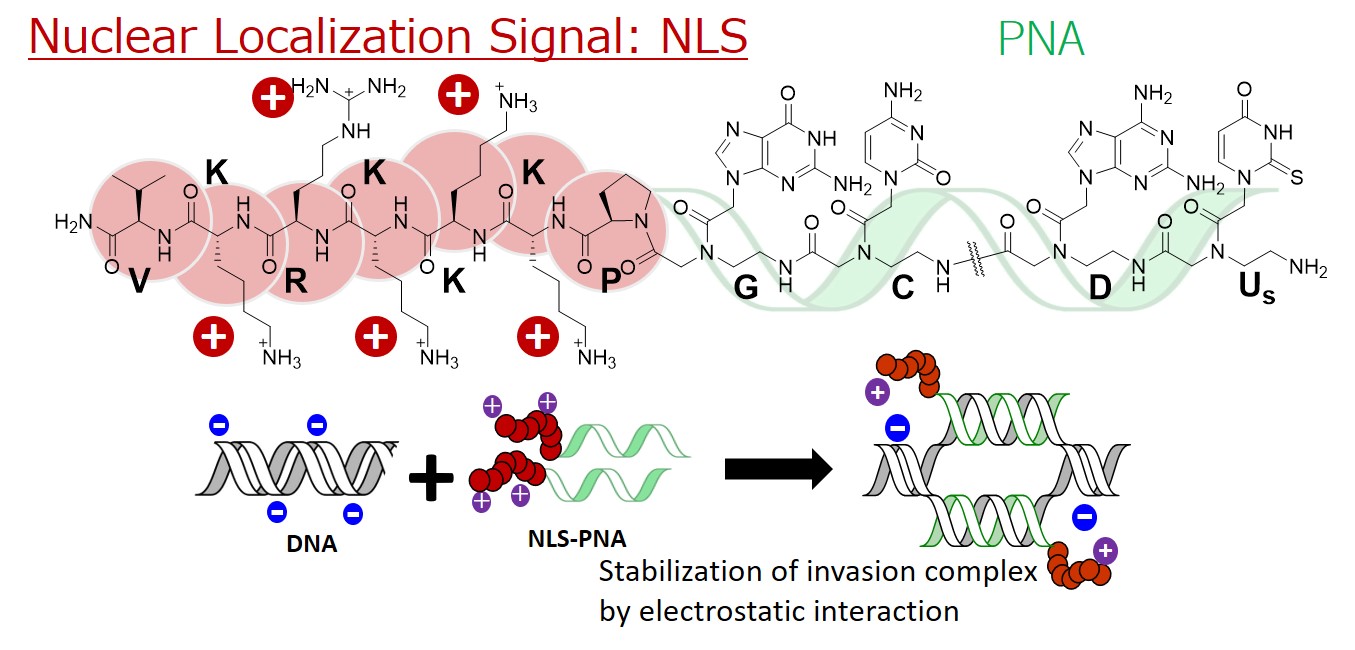
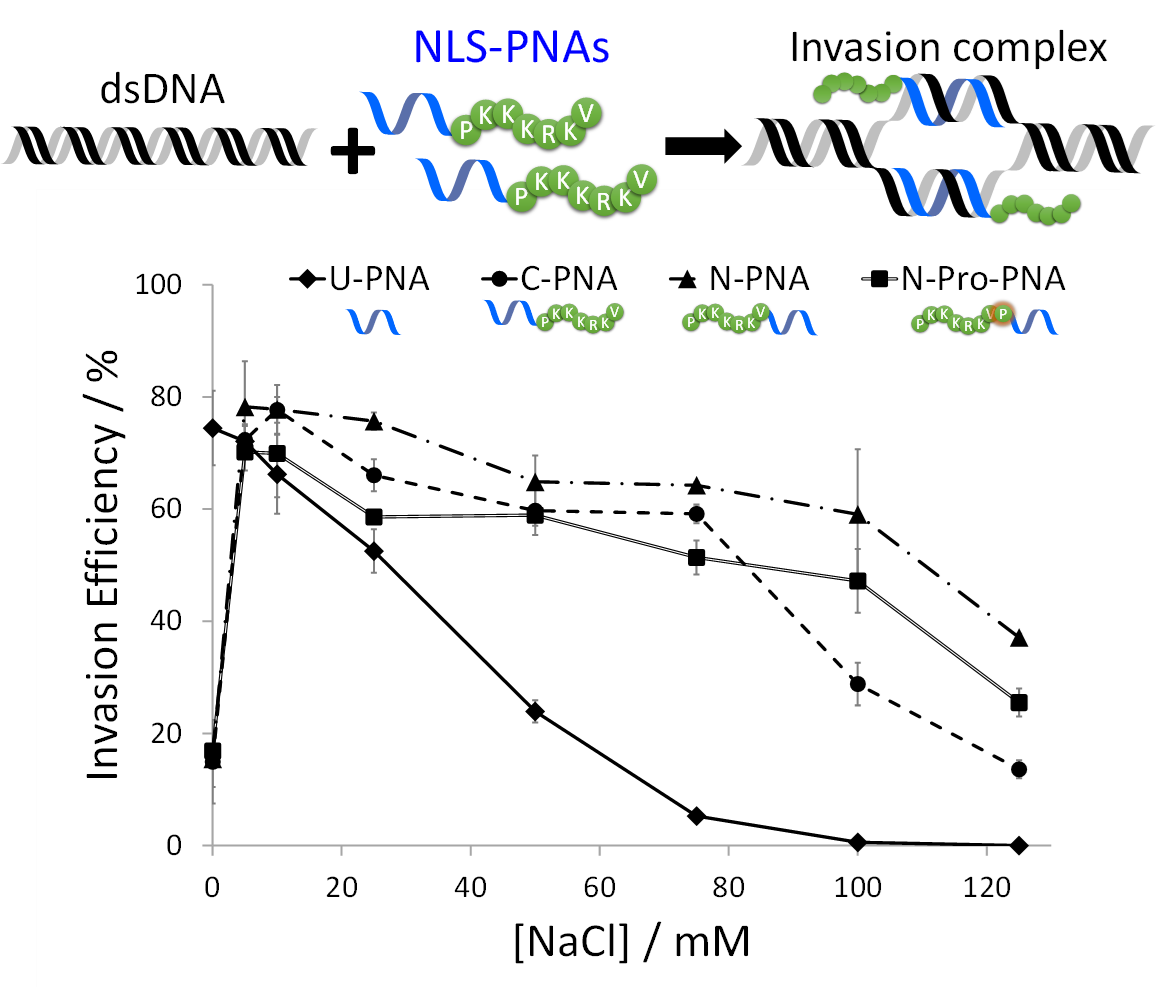
We have previously succeeded in improving the invasion efficiency of PNA based on the electrostatic interaction between PNA and DNA by linking a cationic ruthenium complex (Episode 1: Improvement of PNA invasion efficiency by conjugation with ruthenium complexes) and by introducing cationic properties to PNA by methylating guanine bases (Episode 2: Cationic guanine-introduced PNA (masaPNA) by methylation of guanine). In this study, we have investigated PNA linked with a nuclear localization signal peptide (NLS) as a more straightforward method for improving invasion efficiency.
NLS is a short peptide consisting of cationic amino acids such as Lys and Arg. It is a peptide sequence that functions as nuclear localization in vivo. PNA has a peptide-like backbone synthesized by general solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS). Therefore, NLS and PNA can be easily linked by peptide bonds through SPPS. NLS-linked PNA stabilized the PNA invasion complex due to the electrostatic interaction between the positive charge of NLS and the negative charge of DNA. Interestingly, PNAs with a repeating sequence of simple cationic amino acids such as polylysine also strengthen nonspecific binding to DNA. In contrast, NLS-linked PNAs can form stable invasion complexes while maintaining sequence specificity. This result suggests that NLSs selected during the biological evolution process may have structures and physical properties suitable for interaction with DNA.
Please refer to this paper for details.
- Y. Aiba, G. Urbina, M. Shibata, O. Shoji "Investigation of the Characteristics of NLS-PNA: Influence of NLS Location on Invasion Efficiency" , Appl. Sci., 10, (2020) 8663.
https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238663
Episode 4: Highly efficient invasion of mismatched PNA into mismatched sites of double-stranded DNA


